Highly Stiff Linear Axis for Optics
Precision Assemblies and Components
782416:004.24
Construction of a flying telescope
The Max Planck Institute has built a helium-balloon borne telescope in the Sunrise project. This telescope hung from the balloon by means of a rope and ascended to heights of up to 24000m. The atmosphere is very thin at this altitude, and the conditions are similar to those in space. Such a balloon mission, however, costs only a fraction of a rocket launch with a conventional satellite, and represents an interesting alternative to space travel. Since the telescope hangs only on a rope, it bends due to gravity. Spherical mirrors were used, so that the bend of the optics could be compensated by simply shifting the optical components. The correction movements were achieved by the positioning systems shown here.
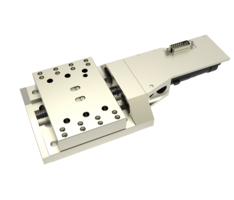
System with short strokes and excenter drive
The so-called M3 mechanism adjusts the tertiary mirror in the longitudinal direction and consists of a conventional carriage system and ball screw drive. For the M2 positioning system, which adjusts the secondary mirror in three translational degrees of freedom, a very short-stroke system based on an excenter drive was developed. Both positioning systems are driven by high-transmission miniature stepper motors with additional encoder feedback.
References
SUNRISE | balloon-borne Solar Observatory | www.mps.mpg.de/solar-physics/sunrise
Verwandte Produkte
Sie suchen eine technische Lösung für Ihre Anwendung?
Jetzt den ersten 3D Entwurf in nur wenigen Tagen erhalten:

Unsere Referenzen